Therapy
ACUPUNCTURE
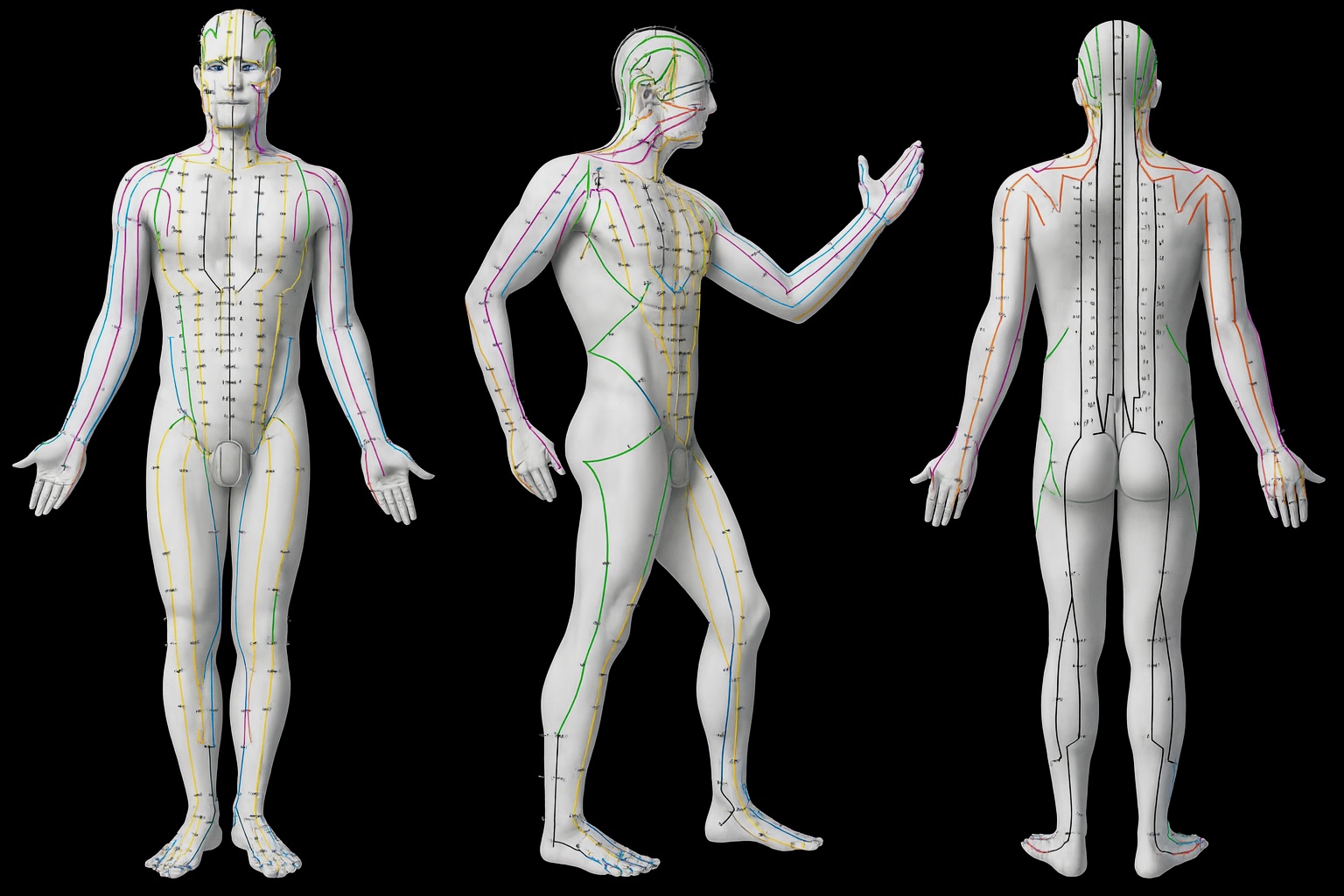
Acupuncture is an empirical medicine that is over 2000 years old. The first written record of it is the “Inner Classic of the Yellow Emperor” (approx. 300 BC), a guide documenting the wisdom of Chinese healing arts. Today, acupuncture enriches the treatment options of “Western medicine” across all cultural boundaries. There are also well-founded scientific studies on numerous indications.
In 1979, the World Health Organization (www.who.int) published a list of indications.
In 1996, the German federal government included needle acupuncture as a medical service in the Schedule of Fees for Doctors (GOÄ). It has been officially recognized as a medical treatment method ever since.
In 2004, the German Medical Association (www.bundesaerztekammer.de) introduced acupuncture as a medical training course with a subsequent examination.
Dr. Merettig and Dr. Stöber hold the B Diploma from the Acupuncture Research Group (www.akupunktur.info) and the German Medical Association for Acupuncture (www.daegfa.de). Dr. Merettig also works as an examiner for acupuncture at the Berlin Medical Association (www.aerztekammer-berlin.de).
CHIROTHERAPY
In orthopedics, this refers to the “adjustment” of vertebrae or joints (of course, the joints—and there are numerous joints in the spine—are not actually dislocated beforehand, meaning they are not “out of alignment”; nor is a nerve literally “pinched.” Often, however, the joints are displaced and locked in this misalignment, stretching the joint capsule, which then results in the often localized and usually radiating pain, especially in the spinal region). You often notice that you have “dislocated” something because the pain appears suddenly, seemingly out of nowhere, for example, while showering or bending over.
But be careful: There are numerous causes for such acute pain. The symptom mentioned is merely an indicator! Whether and how manual therapy can be used in your case should be discussed after a specific manual therapy examination.
CARTILAGE PROTECTION
The knee joint is the most heavily stressed joint in the entire human body. With every step, whether running or climbing stairs, the body’s weight is fully transferred to the knee joint. The upper and lower leg are supported by strong collateral and cruciate ligaments with surrounding muscles. The inner and outer menisci, two crescent-shaped pieces of fibrocartilage, provide cushioning. Joint mobility is ensured by the cartilage coverings on the underside of the femur, the top of the tibia, and the back of the patella, as well as by the synovial fluid, the viscous joint fluid.
Osteoarthritis:
Joint wear and tear ranks second only to heart disease in European disease statistics. In Germany, an estimated 10 million people live with osteoarthritis. This widespread disease causes direct costs of approximately 3 billion euros annually. Consequently, patients frequently ask their orthopedic surgeons: “Doctor, what can I do about my osteoarthritis?” or “How can I get rid of the joint pain?” The question “Can I stop or prevent osteoarthritis?” is being asked more and more frequently.
Therapy: A sterile pre-filled syringe (medical device) is inserted into the knee joint as an intra-articular injection. It contains non-animal, high-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid gel in a particularly pure and viscous form of very high quality (Non-Animal Stabilized Hyaluronic Acid). One NSHA gel bead consists of approximately 10 billion cross-linked hyaluronic acid molecules with a molecular weight of 1 million Daltons.
Conclusion: Targeted cartilage treatment leads to a reduction in pain during activity and at rest, an improvement in joint mobility, and thus to an increase in physical activity. On average, this joint therapy alleviates osteoarthritis symptoms for 6-12 months. Additional pain medication can be avoided.
SURGERY
We no longer perform our own operations. However, we have approximately 30 years of professional experience as surgeons in clinics and outpatient surgery centers (see CVs). We maintain close contact with the best current surgical specialists in Berlin and throughout Germany (neurosurgeons, shoulder, hip, and knee specialists, hand and foot surgeons).
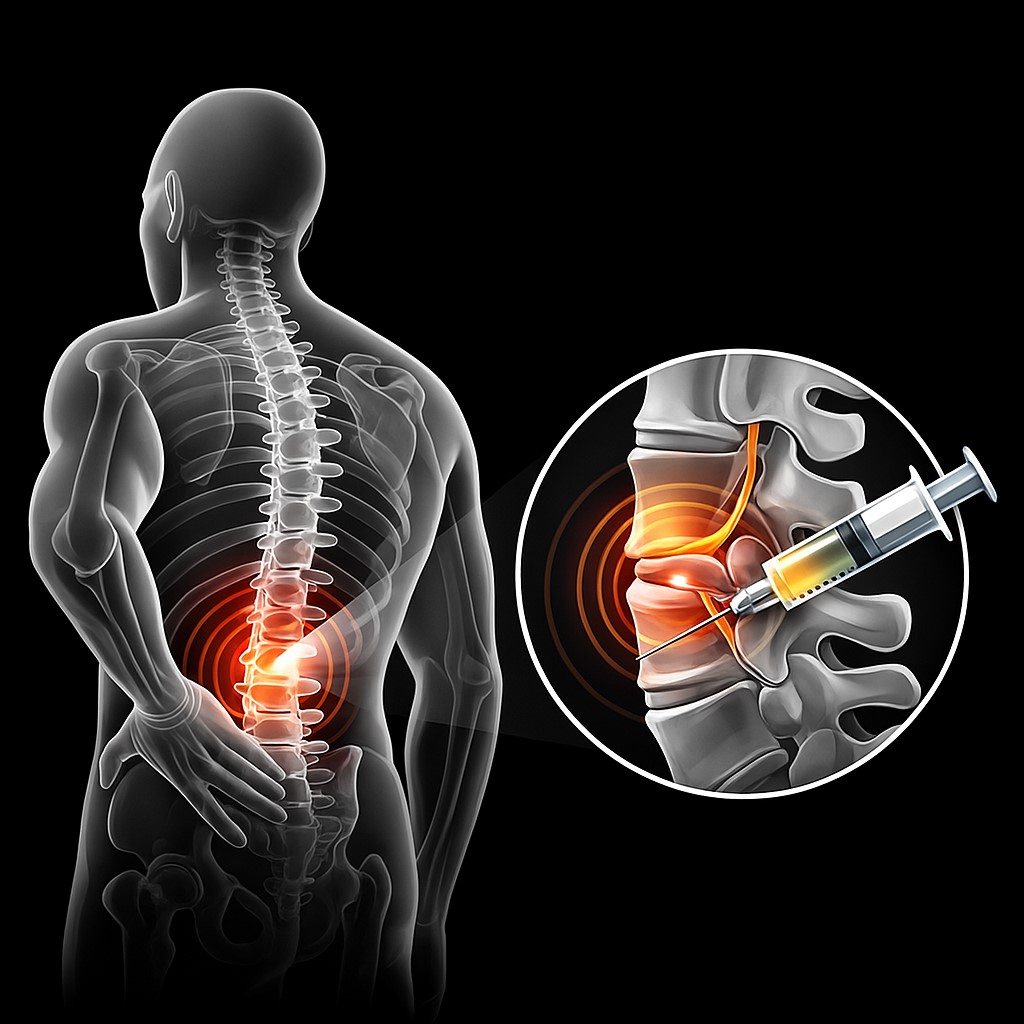
PAIN THERAPY
Pain is an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with acute or potential tissue damage. The word “pain” comes from the Greek language and means “terrible,” “horrible,” or “agonizing.”
Pain experiences are always subjective and emotional. A distinction is made between acute pain, which represents a biological warning function of the body, and chronic pain. The latter is pointless pain without function. It is important to combat it in a timely manner to prevent the development of a so-called “pain memory.”
Dr. Christian Merettig has held the additional qualification “Special Pain Therapy” from the Berlin Medical Association, a public corporation, since January 2001.
Special pain therapists are physicians who, based on particular knowledge and experience, including work in a hospital pain clinic, are qualified to treat acute and chronic pain.
SHOCKWAVE THERAPY
Extracorporeal focused shockwave therapy (ESWT) has developed into a groundbreaking new form of treatment in orthopedics in recent years.
Using high-energy sound waves, patients for whom conservative treatment options have been exhausted can be treated. In most cases, the patient can avoid surgery. Shockwaves are acoustic sound waves that are precisely focused at a specific point (focus) where they exert their effect. Shockwave therapy is a tissue-sparing treatment that is performed on an outpatient basis and spares the patient the need for surgery.
Recent systematic reviews and meta-analyses have shown that ESWT leads to improved function and reduced pain in patients with knee osteoarthritis.
The following conditions can be successfully treated with ESWT:
Calcific tendinitis of the shoulder, Knee joint osteoarthritis (gonarthrosis), Tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis),
Golfer’s elbow (medial epicondylitis),
Heel spur (calcaneal periostosis),
Achilles tendon pain (Achilles tendinopathy), Muscle tension (tendomyopathy).
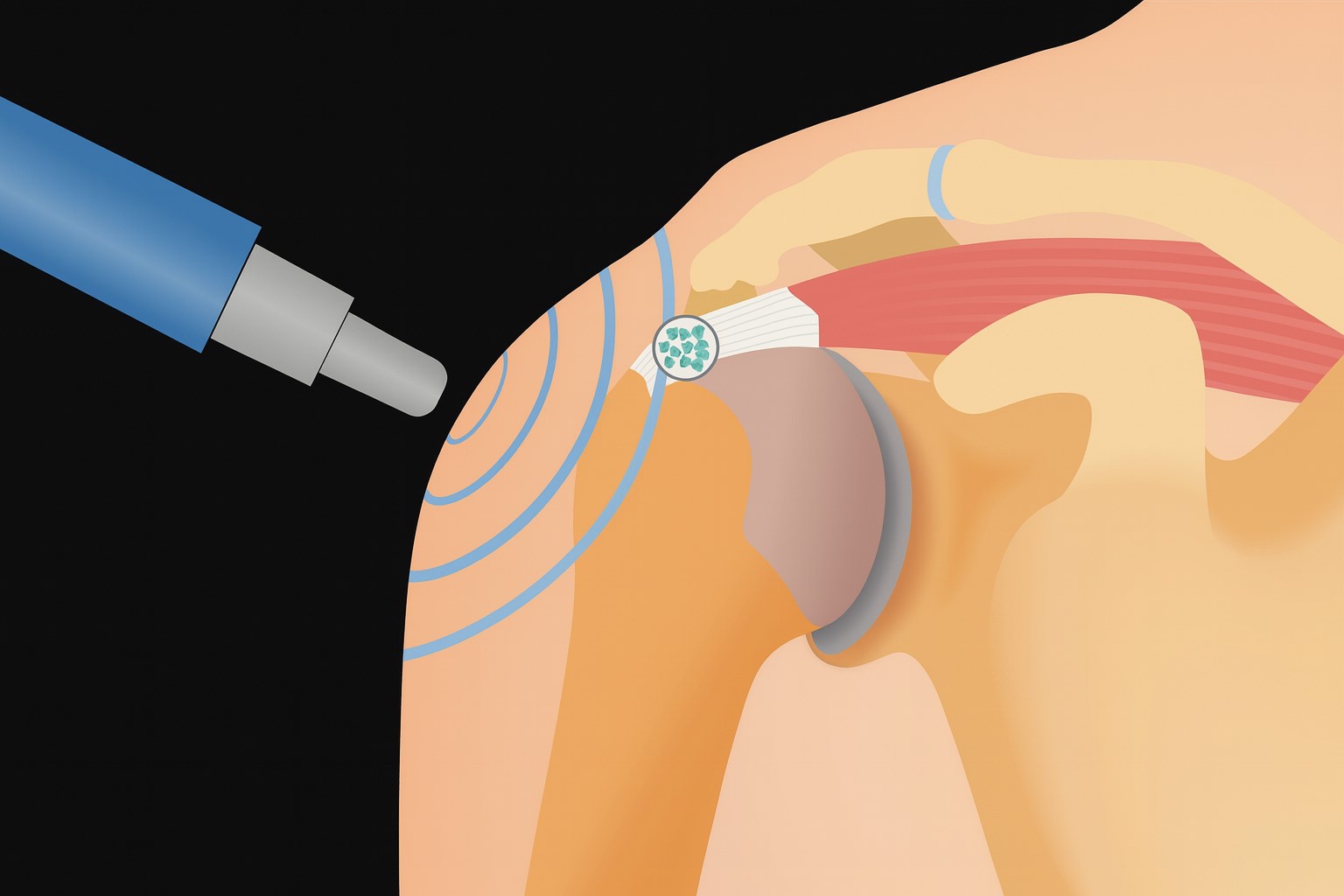
HIGH-DOSE INDUCTION THERAPY
High-Dose Induction Therapy (HDIT) is a novel form of tissue treatment and pain therapy. Electromagnetic fields are capable of stimulating cascades of healing processes in nerve, muscle, connective tissue cells (ligaments, tendons), and blood vessel cells, thereby inducing their regeneration. The targeted application of electromagnetic fields leads to increased capillary growth and thus an increase in the concentration of growth factors in the tissue. Inflammatory processes are minimized (“healing response”).
In many cases, HDIT makes it possible to avoid surgery or reduce pain associated with joint diseases to such an extent that surgery can be postponed. Numerous scientific studies have proven the effectiveness of this form of therapy. HDIT is uncomplicated, with no risks or side effects. Treatments last approximately 20 minutes. As a rule, 3-6 treatments are sufficient.
The following conditions can be successfully treated:
Spinal complaints (cervical and lumbar syndromes), degenerative joint complaints (arthrosis), myofascial pain syndromes, sports injuries, tendon irritation (epicondylitis).
Technical data:
Energy form: induction field, pulse duration: 400 µs, magnetic field intensity: 3.1 Tesla, maximum energy consumption: 2.5 kVA, pulse frequency: 10–100 Hz.
FAT REDUCING INJECTION
Why use fat reducing injections in orthopedics?
Excess weight puts considerable strain on joints, intervertebral discs, and tendons. The latest fat reduction injections offer medically supervised weight loss, thereby relieving strain on the entire musculoskeletal system. This reduces the risk and strain associated with:
- Osteoarthritis (knee, hip, ankle)
- Back pain & herniated discs
- Tendon irritation (Achilles tendon, patellar tendon)
- Foot problems (flat feet, heel spurs)
- Joint inflammation due to excess weight
Advantages for orthopedic patients:
Reduced joint strain (knee, hip, foot, spine). Less inflammation. Preparation for joint surgery (lower risk). Just 1 kg less body weight relieves the knee joints by approx. 4 kg, the ankle joints by approx. 6 kg, and the lumbar spine and intervertebral discs by approx. 8 kg.
Although the fat loss injection is not a painkiller, it is one of the most effective tools for long-term relief of many orthopedic complaints. Less weight = less pain → less pain = better movement → better movement = sustainable health of the musculoskeletal system.
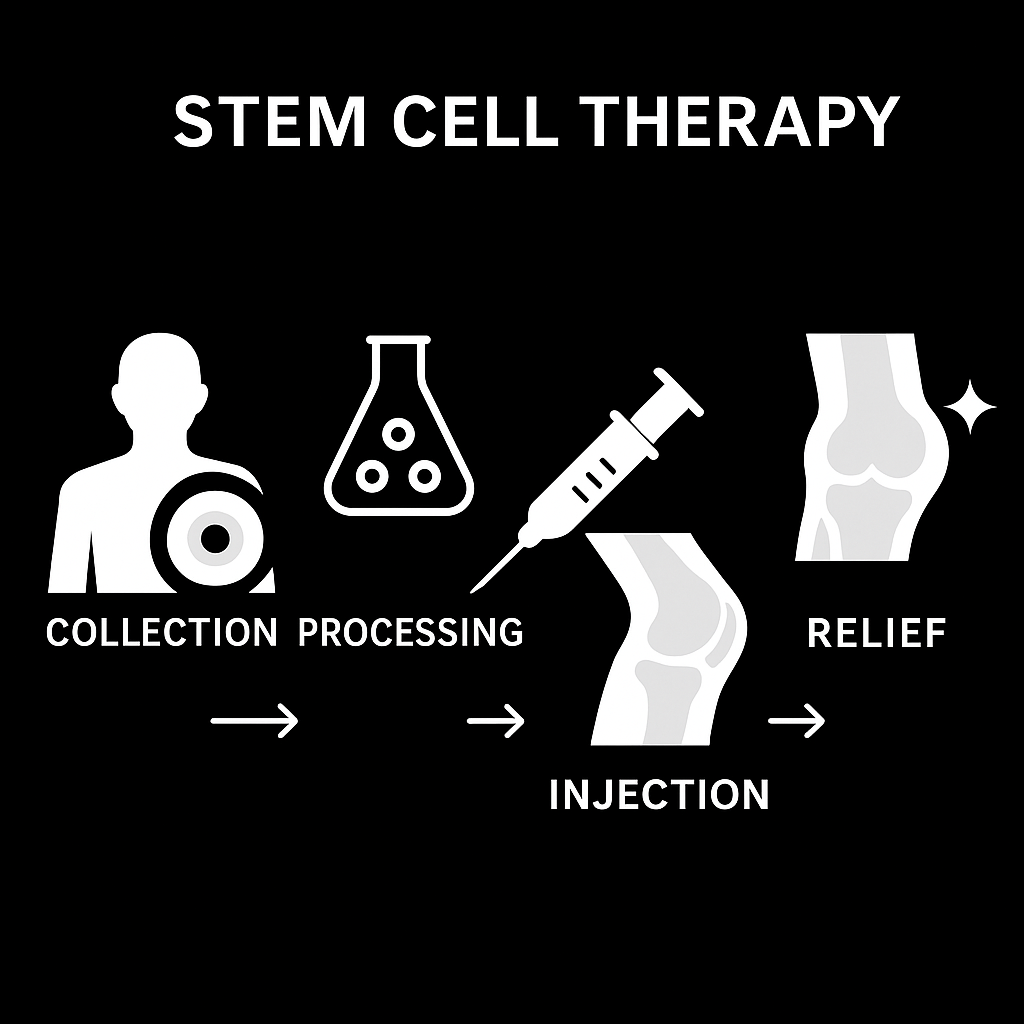
STEM CELL THERAPY
Stem cell therapy (SCT) is becoming increasingly important in modern orthopedics. More and more patients are looking for ways to effectively treat joint problems without having to undergo surgery immediately. This is exactly where stem cell therapy comes in: an innovative approach that specifically activates the body’s natural self-healing powers. The treatment uses the body’s own stem cells from abdominal fat tissue to regenerate damaged joints, reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and improve mobility in the long term. This innovative method is a gentle and sustainable alternative to surgery, especially for degenerative diseases (osteoarthritis)!
Stem cells are cells that can renew themselves and develop into different cell types. There are different types, e.g.: embryonic stem cells (pluripotent – can form almost all cell types), adipose stem cells (fat tissue stem cells = adipose-derived stem cells = ADSC) and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells) – artificially reprogrammed body cells. Adipose stem cells from fatty tissue (e.g., abdomen, thighs) are: particularly easy to obtain (via liposuction), abundant (much more so than in bone marrow) and multipotent → they can develop into different cell types: fat, muscle, bone, cartilage, vascular or skin cells.
Like all stem cells, adipose stem cells release tiny exosomes. These contain growth factors (e.g., VEGF, TGF-β, FGF), microRNAs that control cell processes, and anti-inflammatory signaling molecules. Exosomes are tiny extracellular vesicles (30–150 nm in size) that are released by almost all cells, including stem cells. They contain biologically active molecules such as proteins, lipids, mRNA, and microRNA. These small “communication packages” transport information between cells—a kind of biological courier service. They stimulate cell growth, cell repair, and inflammation inhibition and have an immunomodulatory effect, so they regulate the immune system.